Actin Ab-5 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: C4/ACTIN, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
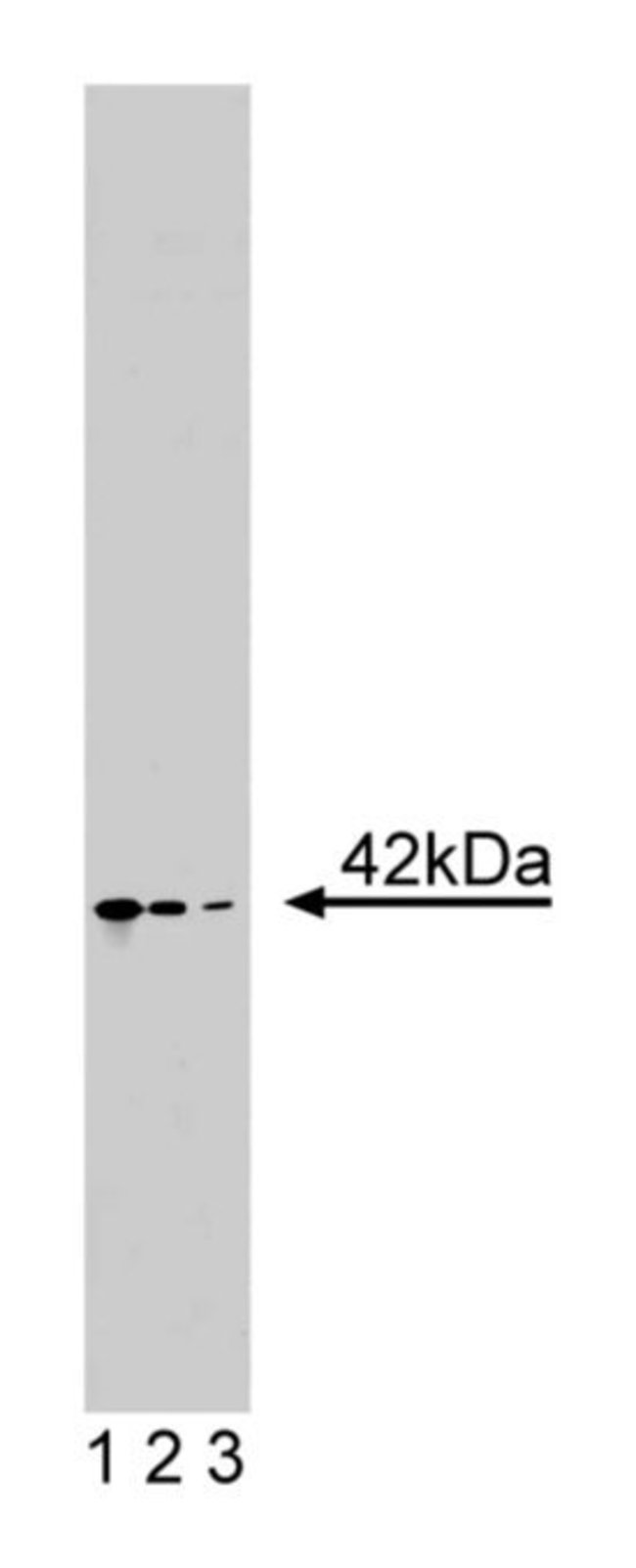
Changes in cellular morphology, adhesion, and motility occur through the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. This reorganization of actin filaments results from interactions between actin and actin-binding proteins. Actin is a 42kDa protein that is known as G-actin in its monomeric form. Polymerization of G-actin monomers leads to the generation of flexible filaments, 5-9 nm in diameter, called F-actin. F-actin may be organized in linear bundles called stress fibers or in two-dimensional networks. The latter are highly concentrated beneath the plasma membrane and form the actin cortex. Regulation of actin cytoskeletal dynamics occurs through actin-binding proteins. These proteins bind to G- and/or F-actin and regulate various aspects of actin cytoskeletal dynamics, such as polymerization and depolymerization of actin, cross-linking of actin filaments into bundles, interaction of actin-based structures with membranes and other cytoskeletal elements, and locomotion of actin-based structures. Thus, the actin cytoskeleton is a complex matrix consisting of G- and F-actin along with the multitude of interactions between these actin forms and a variety of different types of actin-binding proteins. The C4 monoclonal antibody reacts with all known isoforms of actin in vertebrate muscle and non-muscle cells.Immunofluorescence, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135616 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 612657 |
