Cyclin B1 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: GNS-1, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
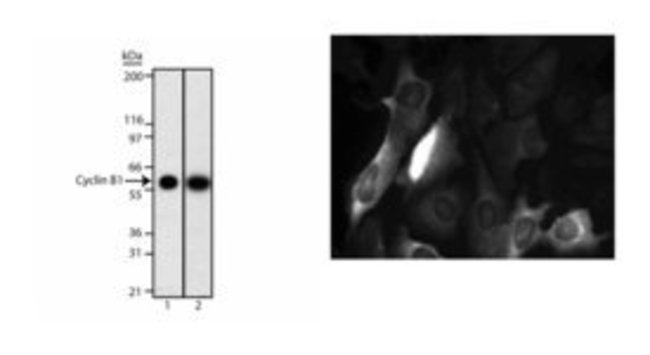
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) are evolutionarily conserved proteins that are essential for cell-cycle control in eukaryotes. Cyclins (regulatory subunits) bind to cdks (catlytic subunits) to form complexes that regulate the progression of the cell cycle. The main cyclin-cdks complexes formed in vertebrate cells are cyclin D-cdk4 (G0/G1), cyclin E-cdk2 (G1/S), cyclin A-cdk2 (S) and cyclin B1-cdk1 (G2/M). These complexes are regulated by activating and inhibitory phosphorylation events, as well as by interactions with small regulatory proteins, such as p21 and p27 [Kip1]. Cyclin B1 is a mitotic cyclin, where expression is normally low in G0/G1, increases in S and is maximal during the G2/M phase. Cyclin B1 is rapidly degraded at the end of mitosis, and is required for cells to exit from mitosis. This antibody has been reported to react to hamster and mouse cyclin B1. In addition, the GNS-1 antibody has been reported to recognize an epitope between amino acids 1-21 of human cyclin B1.Host Species: MouseClone: GNS-1Isotype: IgG1Species Reactivity: HumanImmunogen: Human Cyclin B1 Recombinant ProteinFormula Weight [Chemical]: 62kDaBioimaging, Flow Cytometry, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry (Frozen), Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10133586 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352200 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 554177 |
