Disabled-2/p96 Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 52, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
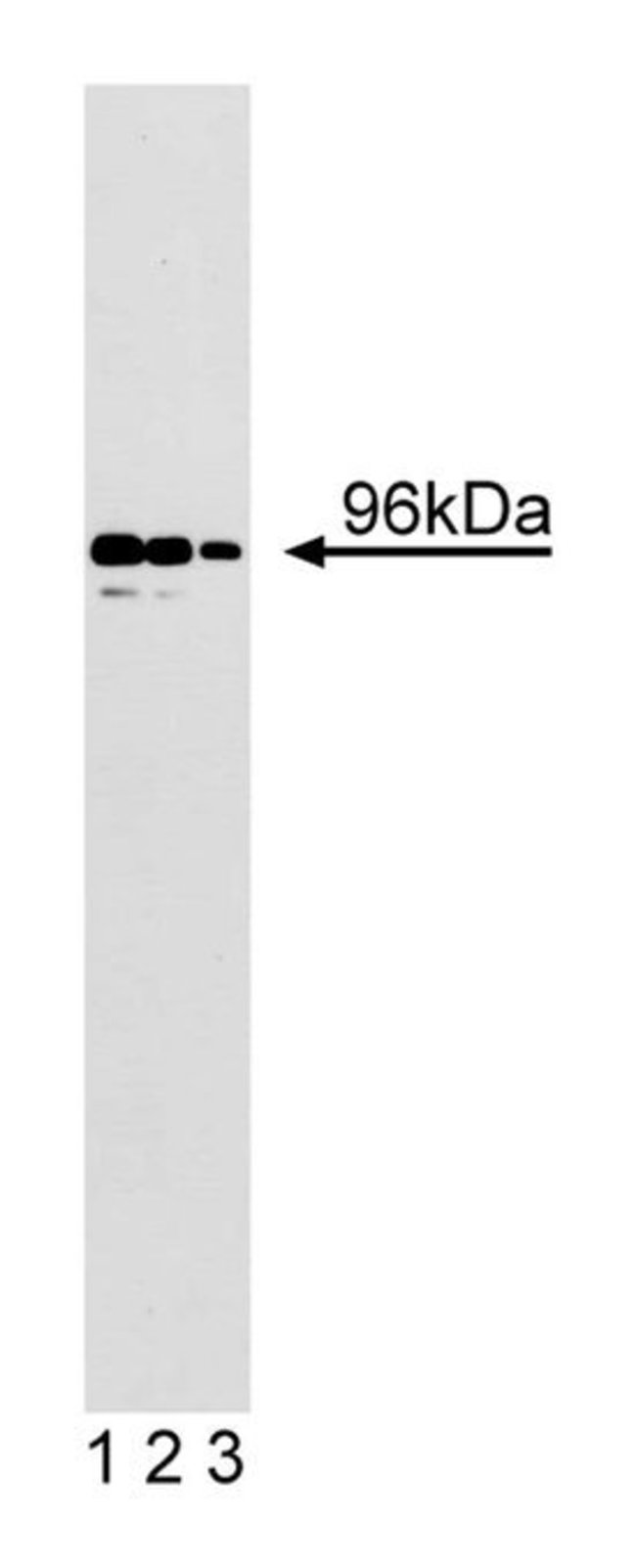
CSF-1 is a growth factor that stimulates the growth and differentiation of immature lymphocytes and is required for the survival of mononuclear phagocytes. Binding of CSF-1 induces dimerization and autophosphorylation of its receptor. This results in the activation of several signal transduction pathways. A unique 96 kDa protein is a component in the CSF-1 signal transduction cascade. p96 is phosphorylated on serine following mitogenic stimulation of a mouse macrophage cell line. p96 contains three potential C-terminal ERK kinase phosphorylation sites, as well as several proline-rich sequences that are potential binding sites for SH3-containing proteins. Structural similarities have been found between p96 and Dab, a product of the Drosophila disabled gene, and p96 was also identified as Disabled-2 (Dab-2) and as differentially expressed in ovarian β receptor to the Smad family of transcription factors. Thus, Dab-2/p96 is an important adaptor molecule in growth factor signaling pathways.
Additional Information
| SKU | 10134983 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610464 |
