PCNA Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 24, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
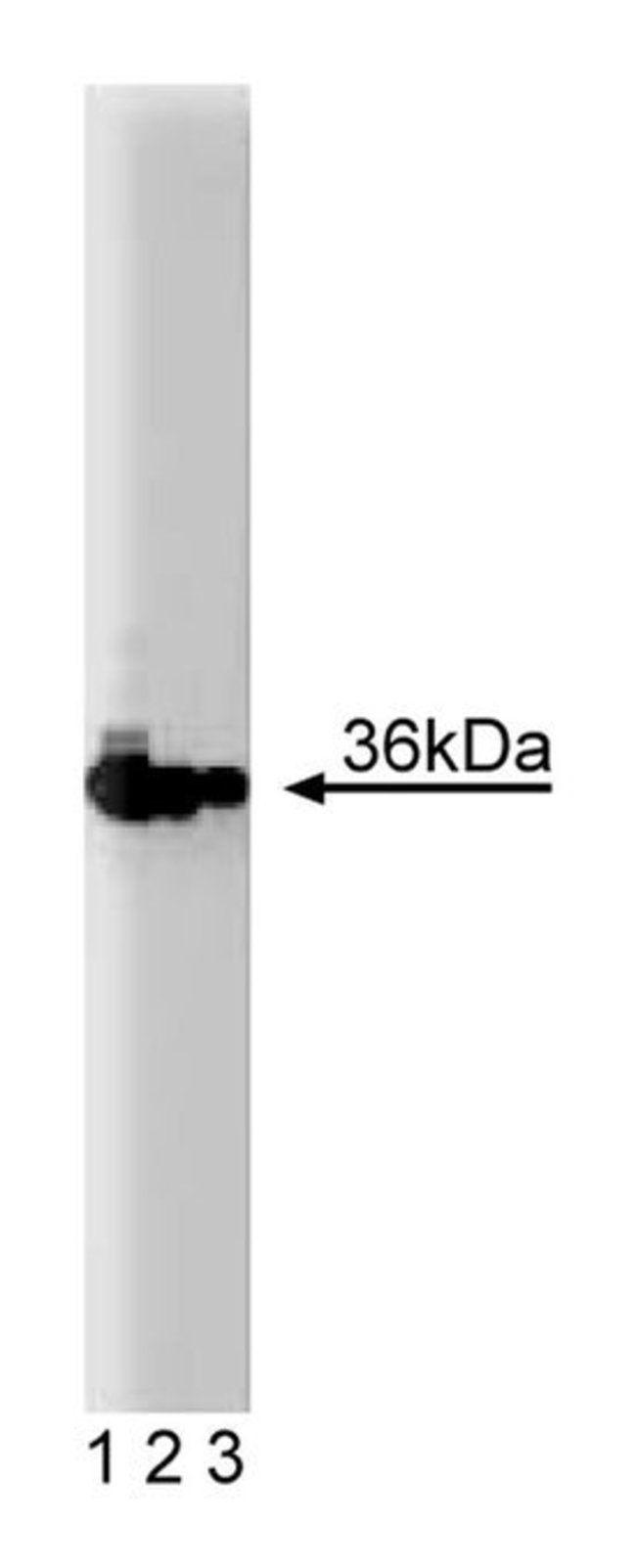
Progression of the mammalian cell cycle is regulated in two different ways: 1) phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of key proteins, 2) synthesis and degradation of regulatory factors. The Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA) was initially identified as a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells and was subsequently described as a subunit for DNA polymerase δ. Human PCNA is 262 amino acids with an apparent molecular weight of 36kDa. PCNA protein levels peak during the S-phase of the cell cycle, at which time it forms a complex with the p21 inhibitor. PCNA is almost undetectable in other phases of the cycle. Because of its unique expression, PCNA has been extensively used in studies associating the prognosis of tumor progression and neoplastic proliferation.Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10135073 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610664 |
