VASP Mouse, Unlabeled, Clone: 43, BD, Mouse Monoclonal Antibody, Each
Details:
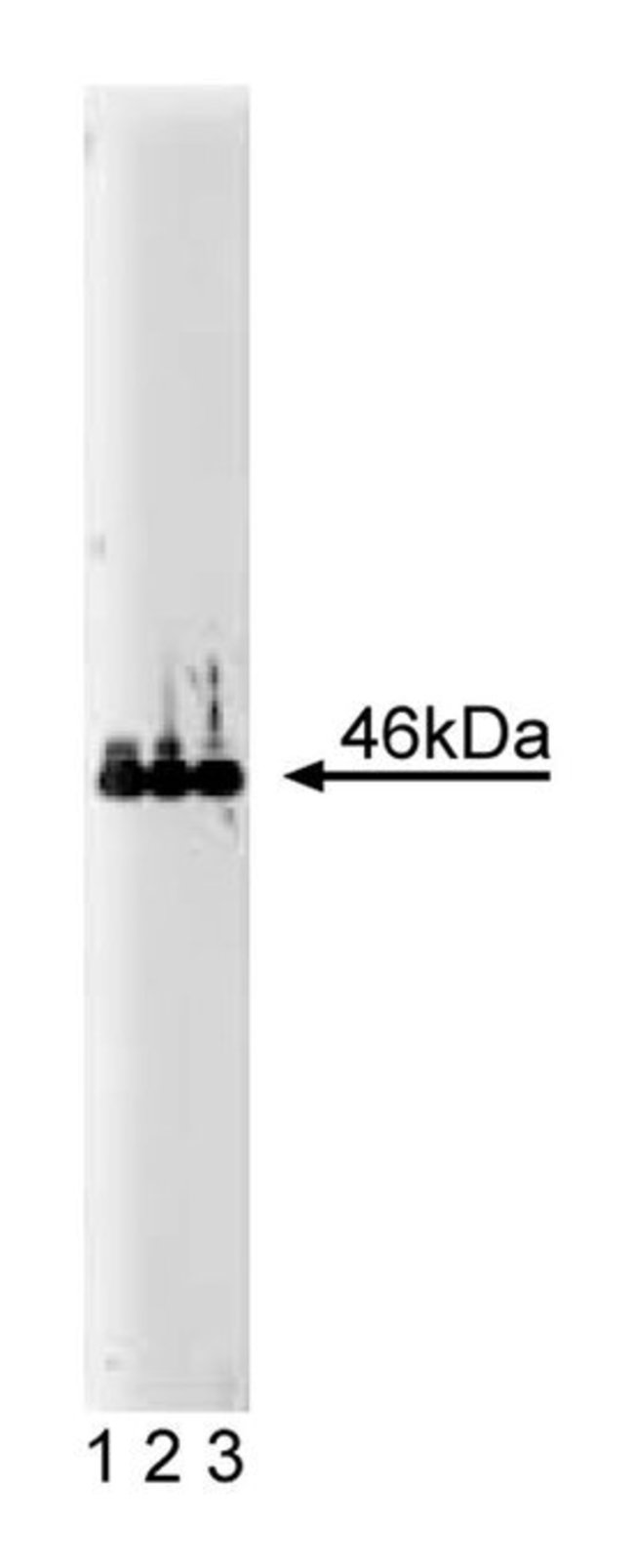
Vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), a substrate for cAMP- and cGMP-dependent kinases, is associated with actin filaments, focal adhesions, and dynamic membrane regions. VASP is composed of several distinct domains: a central L-proline-rich domain contains a GPPPPP motif as a single copy and as a three-fold tandem repeat, as well as three conserved phosphorylation sites for cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases (Ser157, Ser239, and Thr278). A C-terminal domain contains a repetitive mixed-charge cluster which is predicted to form an α-helix. The C-terminal domain appears to be responsible for anchoring at focal adhesion sites. VASP has been shown to be a ligand for profilins. Profilins bind to the poly-L-proline motifs of VASP and it is postulated that these two molecules act in concert to convey signal transduction to actin filament formation.Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation, Western Blotting
Additional Information
| SKU | 10134971 |
|---|---|
| UOM | Each |
| UNSPSC | 12352203 |
| Manufacturer Part Number | 610447 |
